A DOE, diffractive optical element, sometimes referred to as diffractive optical lens, is an optical device used in laser systems to alter the phase of the light passing through it, in a manner that affects the light’s intensity profile and distribution. The generated illumination profile going out of the diffractive optical lens (the light’s shape and angular intensity) will have different characteristics than those of the input beam, as determined by the optical function of the diffractive optical element design.
Diffractive optical elements functionality
The optical functions achievable with diffractive optical elements can be divided into 3 main categories, that refer to the output of the DOE:
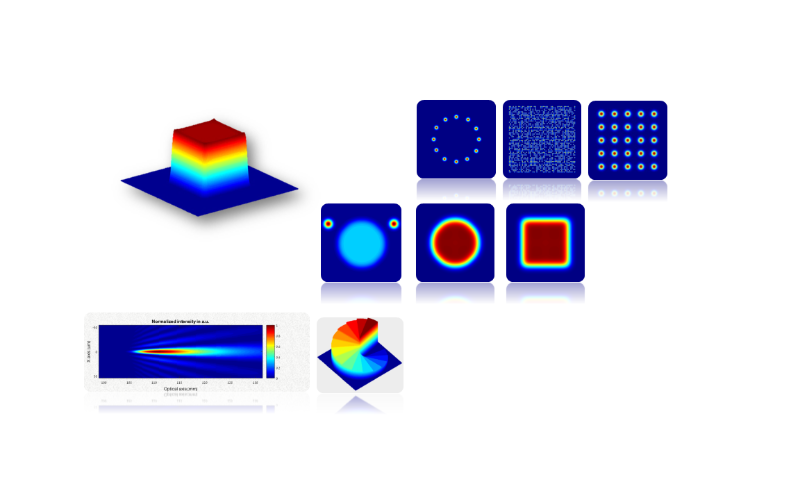
- Beam splitting – Diffractive beam splitter elements split an input beam into any desired number of output beams, in a variety of available arrangements, and with controlled separations. The beam splitter’s output beams will all share the same intensity distribution, similar to that of the input beam, making them a powerful tool for increasing systems throughput.
- Spatial beam shaping – Spatial beam shaper elements modify the beam’s profile and intensity distribution, from any initial profile at the input to the desired well-defined geometrical or free-form shape at the output with sharp borders and a uniform energy distribution within the generated shape. There are generally 3 different types of spatial beam shapers which differ from each other by their principle of operation:
- Top-Hat diffractive beam shapers – Top-hat beam shapers are analytical elements designed to shape highly coherent laser beams to a desired shape with a uniform energy distribution while avoiding speckles. Top-hats are often fabricated on the flat side of a plano-convex lens making them an extremely accurate and compact shaping solution.
- Diffractive diffusers – Diffractive diffusers are periodic beam shapers designed to accurately shape highly multimode beams into a uniform energy distribution, enabling a homogenic treatment or process over a designated area, all using an easy to integrate diffractive optics lens.
- Broadband Diffusers – broadband diffusers are a type of microlens array with a pseudo-random lenslet arrangement, varying heights and 100% packing ratio, making them an excellent, super-efficient uniform beam shaping solution, especially where a wide spectrum beam source, or multiple wavelengths are used.
- Focal beam shaping – Focal beam shaper elements are a family of diffractive optical elements whose functions modify the beam’s properties on its propagation axis. The main two functions that can be achieved with focal beam shapers are either “stretching” the beam waist with an elongated focus element, or separating it to multiple focus planes with a multifocal DOE. These solutions are only applicable in transparent materials. Holo/Or has developed an optical module based on these concepts into a perfect, easy to integrate solution for laser glass cutting.
Generally, all DOEs can be customized and, in many cases, multiple optical functions can be designed to be generated together by a single diffractive surface
Laser applications using diffractive optical elements
The increasing availability of laser power, along with the continuing reduction in laser price-per-Watt, enables a wide variety of applications now having redundancy in power density, to split the beam to increase throughput or shape it to improve accuracy, increase treatment or sample area, or otherwise improve system’s performances. Some of these applications include industrial macro and micromachining processes, glass cutting, aesthetic treatments and medical procedures, sensing and vision applications, metrology, microscopy and other scientific applications and many more.
Advantages of using diffractive optics lenses in laser systems
Diffractive optical elements are fabricated from optical windows, meaning they are flat, small and lightweight, which makes them a useful go-to solution where compactness is of the essence. They offer complex optical functions with flexible properties, which otherwise requires highly complex and expensive optical setups, and sometimes are completely not achievable in any other method. Read our extensive guide to the advantages of DOEs for different use cases
TL; DR - Q&A
What is a diffractive optical element?
A DOE is an optical device used in laser systems to alter the phase of the light projected through it, in a manner that affects the projected light’s intensity profile and distribution
What optical functions can DOEs achieve?
DOEs offer 3 main optical functions, some of which can be convoluted together: beam splitting, spatial beam shaping and focal beam shaping.
What laser applications use DOEs?
Amongst laser applications utilizing DOE are industrial macro and micromachining, glass cutting, aesthetic treatments, metrology, microscopy and more.
What are the distinct advantages of integrating DOEs in laser systems?
DOE are flat, small and lightweight optical components offering complex optical functions with flexible properties, otherwise either requiring highly complex and expensive optical setups, or are completely not achievable in any other method.

